Timeline of Major Script Groups
It's UN International Literacy Day!
This timeline shows a very compressed history of writing, organized into major groups of scripts.
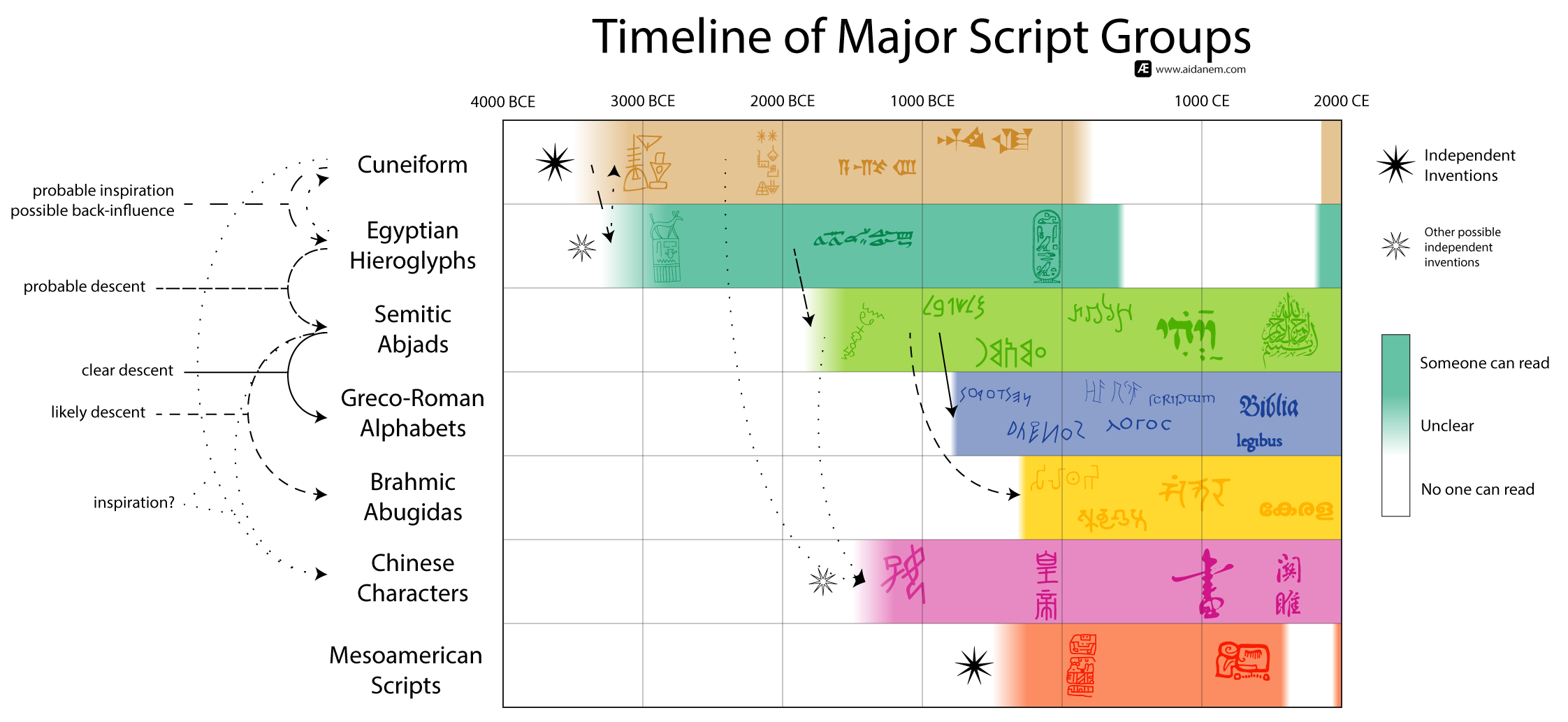
Independent Invention
While many writing systems have been invented over the millennia, very few of them were ever created completely from scratch by people who had never encountered any other writing. There are only two clear examples of such de novo inventions of writing: one in Mesopotamia and/or Egypt and one in Mesoamerica.
Egyptian hieroglyphs are sometimes counted as a separate independent invention of writing, but I think that's not supportable given the proximity in time and space to Mesopotamian cuneiform. There are reasonable discussions to be had about whether that process started in Mesopotamia or Egypt—I say Mesopotamia—but I don't think there's any question that there was influence.
Chinese characters are also sometimes proposed as an independent invention, but again I don't see how that is possible. The Shang Dynasty shows a very similar process of rapid invention of writing as part of a process of defining a national identity as we see in the lead up to First Dynasty Egypt. It would also require assuming that China remained isolated from the international Mediterranean/Western Asia/India trade network for nearly 2000 years, which is practically impossible (China's national myths notwithstanding).
Decipherment
For each cuneiform, hieroglyphs, and Mesoamerican scripts there was a period when working knowledge of the script was lost before being recovered through decipherment in the 19th-20th centuries.
Embedded examples
Each of the images embedded in the timelines is a representation of a specific, preserved piece writing:
- Cuneiform
- Archaic cuneiform tablet of E.A. Hoffman (Proto-cuneiform tablet, Jemdet Nasr period)
- Proto-cuneiform, c. 3000 BCE
- Unicode: ? 𒊩 ?
- Transliteration: ?.SAL.?
- Translation: ? "woman" ?
- Note: I haven't identified the other two archaic signs yet
- Seal of Naram-Sin (Akkadian King)
- Akkadian cuneiform, c. 2250 BCE
- Unicode: 𒀭𒈾𒊏𒄠𒀭𒂗𒍪
- Transliteration: D.na-ra-am.D.EN-ZU
- Translation: "Naram-Sin" (name)
- Amarna Letter EA 161
- Akkadian cuneiform, c. 1350 BCE
- Unicode: 𒀀𒍣𒊒
- Transliteration: a-zi-ru
- Translation: "Aziru" (name)
- Rassam cylinder
- Assyrian cuneiform, 643 BCE
- Unicode: 𒀭𒊹𒆠
- Transliteration: an-šar₂.KI
- Translation: "Assyria" (place name)
- Archaic cuneiform tablet of E.A. Hoffman (Proto-cuneiform tablet, Jemdet Nasr period)
- Egyptian Hieroglyphs
- Stone vase of Seth-Peribsen
- Egyptian hieroglyphs, c 2800 BCE
- Unicode: 𓃩 𓋴𓉐𓄣𓈖
- Transliteration: SET pr-jb.sn
- Translation: "Seth-Peribsen" (name)
- Ebers Papyrus
- Hieratic script, c. 1500 BCE
- Unicode: 𓂻𓊃𓂻𓂋𓆑𓏭 𓂧𓂧𓈖𓈖?𓂝??
- Transliteration: jw-s-jw-r-fy-dd-nn?-ꜥ?
- Translation: ??
- Note: I can't read hieratic and haven't found a detailed translation of Ebers
- Painted wooden box from the tomb of King Tutankhamun
- Egyptian hieroglyphs, c 1327 BCE
- Unicode: 𓅭𓇳 𓇋𓏠𓈖𓏏𓅲𓋹𓋾𓉺𓇗
- Transliteration: zꜣ-rꜥ jmn-twt-ꜥnḫ-ḥqꜣ-jwnw-šmꜥw
- Translation: "Son of Ra Living-Image-of-Amun-Ruler-of-the-Pillar-of-Upper-Egypt" (Tutankhamun)
- Victory Stele of Piye
- Egyptian hieroglyphs, c 719 BCE
- Unicode: 𓇓𓏏𓆤𓏏
- Transliteration: nswt-bjtj
- Translation: "He of the Bee and Reed, Dual-King" (title)
- Cartouche of Cleopatra
- Egyptian hieroglyphs, c. 30 BCE
- Unicode: 𓈎𓃭𓇋𓍯𓊪𓄿𓂧𓂋𓄿𓏏𓆇
- Transliteration: qljwꜣpꜣdrꜣ-FEM / kliwapatra-FEM
- Translation: "Cleopatra" (name)
- Stone vase of Seth-Peribsen
- Semitic Abjads
- Wadi el-Hol inscription
- Proto-Sinaitic script, c. 1800 BCE
- Unicode: 𐤌𐤔𐤕 𐤓 𐤄 or 𓈖𓇨𓏴 𓁶 𓀠
- Transliteration: mšt r h
- Translation: "Excellent b(anquet) (of the) c(elebration)?"
- Ahiram sarcophagus
- Phoenician script, c. 850 BCE
- Unicode: 𐤌𐤋𐤊 𐤂𐤁𐤋
- Transliteration: mlk gbl
- Translation: "King of Gebal (Byblos)"
- Sabaean votive stele (Panel Almaqah Louvre DAO18)
- Ancient South Arabian script, c. 500 BCE
- Unicode: 𐩲𐩣𐩱𐩣𐩧
- Transliteration: ʕmʔmr
- Translation: "Ammî'amar" (name)
- Palmyrene Grand Colonnade dedication
- Palmyrene Aramaic script, c. 250 CE
- Unicode: 𐡲𐡫𐡬𐡶
- Transliteration: ṣlmt
- Translation: "statue, image"
- Aleppo Codex
- Aramaic Square script (Hebrew script), c. 920 CE
- Unicode: וַיְהִי
- Transliteration: vayhí
- Translation: "it happened that, now"
- Ottoman Thuluth Basmala
- Thuluth script (Arabic script), c. 920 CE
- Unicode: بِسْمِ ٱللَّٰهِ ٱلرَّحْمَٰنِ ٱلرَّحِيمِ
- Transliteration: bi-smi llāhi r-raḥmāni r-raḥīm
- Translation: "In the name of God, the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful"
- Wadi el-Hol inscription
- Greco-Roman Alphabets
- Pithekoussai Nestor Cup
- Western Archaic Greek script, c. 710 BCE
- Unicode: ΝΕΣΤΟΡΟΣ
- Transliteration: Nestoros
- Translation: "Nestor" (name)
- Duenos inscription
- Old Italic script, c. 600 BCE
- Unicode: 𐌃𐌖𐌄𐌍𐌏𐌔
- Transliteration: Duenos
- Translation: "good"
- Vimose comb
- Germanic runes, c. 160 BCE
- Unicode: ᚺᚨᚱᛃᚨ
- Transliteration: harja
- Translation: "Army" or "Warrior" (possibly a name)
- Codex Sinaiticus
- Byzantine uncial (Greek alphabet), c. 350 CE
- Unicode: ΛΟΓΟϹ
- Transliteration: logos
- Translation: "word, speech, reason"
- Book of Durrow
- Insular script (Latin alphabet), c. 700 CE
- Unicode: scriptum
- Transliteration: scriptum
- Translation: "text, writing"
- engraved type of Nicholas Jenson
- Humanist typeface (Latin alphabet), 1472 CE
- Unicode: legibus
- Transliteration: legibus
- Translation: "laws"
- Gustav Vasa Bible
- Fraktur blackletter (Latin alphabet), 1541 CE
- Unicode: Biblia
- Transliteration: Biblia
- Translation: "bible, books"
- Pithekoussai Nestor Cup
- Brahmic Abugidas
- Pillars of Ashoka
- Ashokan Brahmi script, c. 230 CE
- Unicode: 𑀲𑀺𑀮𑀸𑀣𑀪𑁂
- Transliteration: Silā Thabhe
- Translation: "stone pillars"
- Bhitari Pillar inscription
- Gupta Brahmi script, c. 460 CE
- Unicode: 𑀲𑁆𑀓𑀦𑁆𑀤𑀕𑀼𑀧𑁆𑀢
- Transliteration: Skandagupta
- Translation: "Skanda Gupta" (name)
- Tang Dynasty Pratisara mantra
- Siddham, 927 CE
- Unicode: 𑖦𑖽𑖝𑖨
- Transliteration: mantra
- Translation: "mantra, prayer"
- High Court of Kerala marqee
- Malayalam script, c. 2000 CE
- Unicode: കേരള
- Transliteration: kēraḷa
- Translation: "Kerala" (place name)
- Pillars of Ashoka
- Chinese Characters
- Shang oracle bone fragment
- Oracle bone script, c. 1100 CE
- Unicode: 子女
- Transliteration: Old Chinese *ʔslɯʔ naʔ (Pinyin: zǐnǚ)
- Translation: "children"
- Qin engraved iron weight standard
- Small Seal script, c. 221 BCE
- Unicode: 皇帝
- Transliteration: Old Chinese *ɡʷaːŋ teːɡs (Pinyin: huángdì)
- Translation: "Emperor"
- Letter by Cai Xiang
- Chinese characters, c. 1050 CE
- Unicode: 書
- Transliteration: Middle Chinese ɕɨʌ (Pinyin: shū)
- Translation: "letter"
- Book of Odes calligraphed by Qianlong Emperor
- Chinese characters, c. 1750 CE
- Unicode: 關雎
- Transliteration: guān jū
- Translation: Guan ju (poem title); "guan (cries the) osprey"
- Shang oracle bone fragment
- Mesoamerican Scripts
- La Mojarra Inscription
- Isthmian script (Olmec), 156 CE
- Unicode: —
- Transliteration: ?
- Translation: ?
- Madrid Codex
- Maya script, c. 1300 CE
- Unicode: —
- Transliteration:
- Translation:
- La Mojarra Inscription